What is PRP?
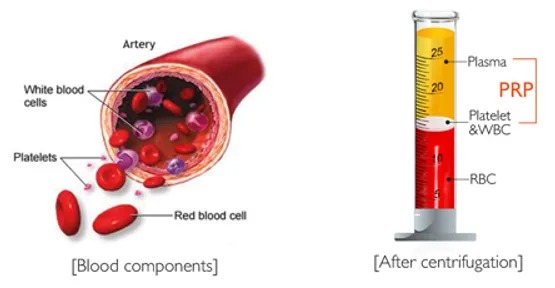
Our blood is made up of 93% red blood cells, 6% white blood cells, 1% platelets and plasma. Platelets are best known for their function of blood-clotting to stop bleeding. Platelets, however, are much more significant than this, as human platelets are also a critical component in injury healing.
Platelet-rich plasma, commonly referred to as PRP, is an autologous blood derivative- it is human blood that is spun down and separated producing a concentration of platelets above normal values. Platelets are the clotting cells of our blood, but they also have great potential in enhancing healing of muscle, tendon, and ligaments. Studies suggest that growth factors released by platelets recruit reparative cells, may augment tissue repair, and accelerate soft tissue healing.